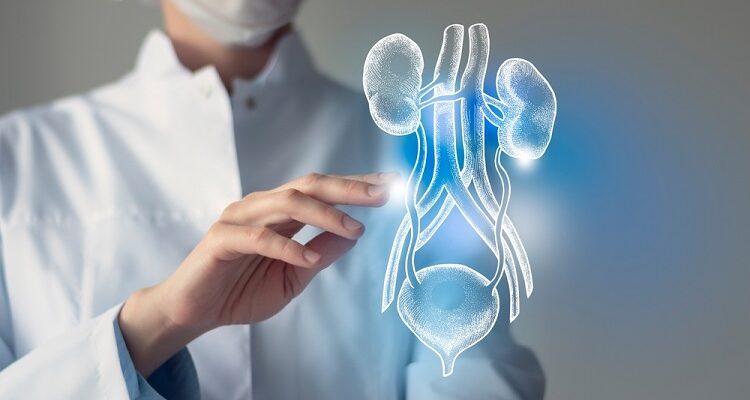
Urinary tract infection is a common condition affecting women at least once in their lifetime. It affects your urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra) causing pelvic pain, urinary incontinence, and high-grade fever.
Richmond UTI care involves discrete diagnosis and prompt treatment to help relieve your symptoms and prevent further complications.
Table of Contents
Possible causes of UTI
UTIs usually occur due to bacterial infiltration (mostly E. coli) through the urethra that may spread to your bladder. The urinary system is designed in such a way it keeps microorganisms away. But, sometimes the defense system may fail causing a full-blown infection in the urinary tract.
Risk factors for UTIs:
- Women are more prone due to shorter urethra
- Being sexually active
- Using diaphragms for birth control
- Post-menopause due to a decline in the estrogen levels
Inflammation in the urethra is termed urethritis, while bladder inflammation is cystitis. Pyelonephritis refers to a kidney infection.
Common symptoms associated with UTI
UTIs cause inflammation of the lining of your urinary tract, causing the following symptoms:
- Pain in the abdomen, pelvis, or lower back
- Cloudy foul smelling pee
- Pink or dark-colored urine
- Frequent urination
- Urinary incontinence
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Blood in your pee (hematuria)
- Pain in your penis
If the infection spreads to the kidneys you may experience the following:
- Fatigue
- High-grade fever
- Chills
- Body pain
- Nausea and vomiting
Infections reaching the kidneys require immediate treatment to prevent complications.
A complicated UTI
This can occur most often due to an infection that does not respond to the usual treatment, kidney infection, compromised immune system, or may occur if you have other health conditions like STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). UTIs occurring in men, and recurrent UTIs in women are also considered complicated UTIs.
Treating UTIs
Most often your healthcare professional may recommend the following treatment options:
Conservative approach
- Hydrating yourself well
- Drinking cranberry juice
- Taking vitamin C supplements to improve your immunity
- Urinating after sexual intercourse
- Not holding your urine for too long
- Avoid diaphragms, and switch to other birth control methods
Medications
- Oral or IV (intravenous) antibiotics to kill the bacteria
- Preventive antibiotics (a single dose) after every sexual intercourse
- Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women
Final note
Urinary tract infections are common medical conditions affecting your urinary system, due to bacterial colonization. This can cause varying symptoms like pelvic and abdominal pain, fever, urinary incontinence, foul smelling urine to name a few. Early diagnosis can pave the way for an effective treatment through lifestyle changes and antibiotics to provide relief from symptoms.






Comments